How Cannabis High In THC Affects the Brain and Body When Ingested or Smoked - WARNING
1). It is first important to know that our bodies produce natural cannabinoids called endogenous (endogenous) cannabinoids.
The brain naturally produces endo cannabinoids (Anandamide & 2-Arachidonoyl Glycerol) from the time we were a foetus to the time we die. The role these play in the brain and body is to regulate biological functions including mood, perception, appetite, the immune system, metabolism, learning, memory, anxiety, growth and development, etc. These endo cannabinoids that are naturally produced interact with cannabinoid receptors through out our brain and body. There are two receptors that the endo cannabinoids interact with called CB1 & CB2 receptors.
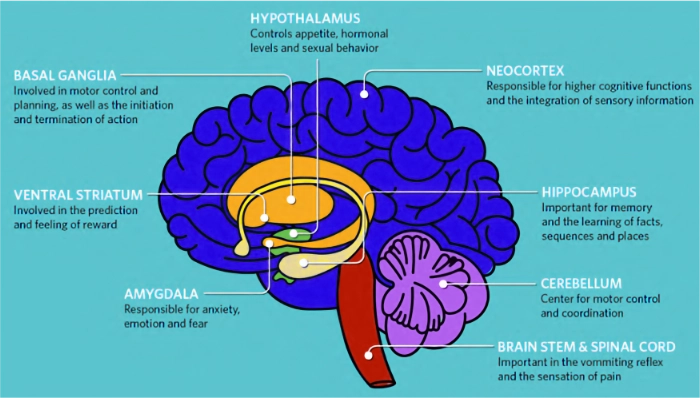
CB1 receptors are mostly found in the nervous system (brain, spinal cord & nerves).
CB2 receptors are also found in the nervous system too but are mostly found in the body tissues that make up the body (immune system, skin, organs, muscles).
So endo cannabinoids interact with our CB1 & CB2 receptors to regulate the electric signal (neurotransmitters) sent between our neuron’s. They can increase or decrease the signal between neuron’s. That act like a natural valve that can open or close to regulate the message being sent from neuron to neuron. Endo cannabinoids also strengthen the bridge between neuron’s helping use to think faster, learn faster, react faster, etc.
2). What happens when we introduce cannabis high in THC?
Cannabis has over 70 cannabinoids but the most common three spoken about and researched are THC, CBD and CBN.
When cannabis is ingested or smoked these cannabinoids bind to the CB1 & CB2 receptors which are designed for our natural endo cannabinoids. The fact is, cannabinoids from cannabis are much more potent than endo cannabinoids created by our brain. Cannabinoids like THC, CBD and CBN bind to the CB1 & CB2 receptors with much more force and affinity. They out compete the endo cannabinoids and stick to the receptors for a long time, especially if you use cannabis regularly. This ultimately can leave our endo cannabinoid system dysfunctional if you are a chronic cannabis user leaving you dependent (addicted) on cannabis use. Cannabinoids are lipophilic which means they are dissolved and stored in fatty tissues. This is not body fat but rather the fatty membrane that coats our neuron’s. When we say cannabinoids hang around a neuron for a long time, you will test positive for having cannabis in your system for up to 2 months after using cannabis. This is a long time and can ruin an athletic career if the athlete uses cannabis on the off season as they may test positive during a drug test. Some companies also do drug tests and as a result you could lose your job for using cannabis on holiday 2 months ago.
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) binds heavily to the CB1 receptor located in our brain and nervous system and is the cannabinoid known to make you high (it is extremely psychoactive). It interferes with our biological functions in the brain including mood (↑), appetite (↑), creativity (↑), learning (↓), memory (↓), anxiety & stress (↓). As you can see by some biological functions increasing and decreasing, cannabis has a seesaw effect. The brain is made up of many different parts that each perform different tasks. Depending on the part of the brain, the activated neuron’s can either increase or decrease output of their electrical signals.
For example; The process that makes anxiety go away: THC binds to the CB1 receptors spread throughout the brain. In the prefrontal cortex the message from the neuron’s tell the prefrontal cortex to increase (↑) output. In the amygdala the message from the neuron’s tell the amygdala to decrease (↓) output. This is what makes you feel calm, or a false security that you are safe leaving you less anxious.
Unlike endo cannabinoids which strengthen the bridge between neuron’s, THC weakens the bridge which could lead to long term issues such as short & long term memory, increased anxiety, mood disorders, slow reaction times and many other unbalanced biological functions.
Many people believe that because we have cannabinoid receptors in our brain and body, it means it is safe or appropriate to smoke or ingest cannabis to target our cannabinoid receptors. This is simply not true. That doesn’t mean that cannabis is a bad idea to smoke or ingest, but it can be dangerous to a certain population of people (heart diseases and mental disorders) both recreationally and medicinally if the cannabis is high in THC. As cannabinoids from cannabis outcompete our natural endo cannabinoids, we can become dependent (addicted) on cannabis. When we suddenly stop the use of cannabis our cannabinoid receptors are no longer stimulated and the symptom that we have been trying to treat becomes much more present.
For example; A lot of people use cannabis to treat anxiety and there is no doubt that cannabis can relieve anxiety. The problem comes when they stop using cannabis! The anxiety that comes after stopping cannabis use can be a lot worst than the anxiety we were trying to treat in the first place. Therefore you go back to cannabis to treat that anxiety = addiction. Another two common side effects of quitting cannabis is extreme mood swings and insomnia. If you are stuck in this cycle, it’s is best to wean down your cannabis use gradually over a period of 3 weeks and then cutting it out completely. It will then most likely take another 3 weeks for your natural endo cannabinoids to regulate biological functions correctly. It will be a difficult 3 weeks and if you battle with discipline or relapse ask a family member or friend to help you through it.
3). Different types of Cannabis
Cannabis exists in three main varieties: Sativa, Indica, and Ruderalis. Hybrid strains, a result of crossbreeding, offer tailored cannabinoid ratios. For most medicinal dispensaries, Ruderalis is not used! Medicinal cannabis, with lower THC levels, was developed from hybrid strains. While it may not induce a high, the presence of cannabinoids, particularly CBD, still impacts the endogenous cannabinoid system, but in a much more predictable way as it mainly binds to the CB2 receptor. This keeps the regulation of the endogenous cannabinoids in your brain active with CB1 receptors, and targets the body tissues that make up the body (immune system, skin, organs, muscles). It still has an impact in your brain and nervous system as CB2 receptors are found in these regions, but are much less populated than CB1 receptors.
4). Conclusion on smoking and ingesting cannabis high in THC
Cannabis & Medicinal Cannabis high in THC do have a soothing effect on the brain and body when smoked or consumed. It can be a euphoric experience and a break from the normal day to day struggle called life. In the long term THC leaves your natural endogenous cannabinoid system dysfunctional leading to addiction. We believe cannabis high in THC should not be smoked or consumed for prolonged periods (chronic use). There are certain circumstances (very limited) that cannabis high in THC should be smoked or consumed to treat chronic conditions. Those chronic conditions are mostly related to issues in the nervous system, such as severe nerve pain, chronic migraines, and diseases in the brain. Understanding the effects of cannabis on the brain and body emphasises the need for responsible usage, particularly for medicinal purposes. Striking a balance between potential relief and the risk of long-term dysfunction of the endo cannabinoid system is essential for informed and safe consumption.
5). How should medicinal cannabis be used?
For medicinal purposes, applying cannabis topically on the skin is more beneficial. The skin contains CB2 receptors, allowing cannabinoids to alleviate chronic symptoms without entering the bloodstream or affecting the brain. The cannabis product that is applied to skin penetrates the epidermis and dermis layers of the skin tissue. This approach avoids impacting the endogenous cannabinoid system, preserving its ability to regulate biological functions effectively. From various research studies its is proven that any cannabis should rather not be smoked, even if that cannabis is low in THC and high in CBD. Smoking (igniting) cannabis has many of the same toxins and carcinogens as smoking tobacco. In some cases cannabis has a positive effect on the lungs such as opening the capillaries, and helping to clear mucus, but it is advised to use a dry herb vaporiser which does not ignite the cannabis but heats it up and you inhale the steam.
For certain chronic conditions medicinal cannabis should rather be ingested in capsule or tincture forms that is made from Full Spectrum CBD that has the correct cannabinoid profile.
At CannaMagic, that is our speciality as we get our different strains of cannabis oil lab tested and then blended together to get the perfect cannabinoid profile. We then infuse this oil into our lotions, topical balms, etc.

